最基本的Socket模型
Socket编程能让客户端和服务器能通过网络通信。Socket编程是进程间通信比较特别的方式,特别之处在可以跨主机通信。关于进程间通信。客户端和服务端要通信,就要各自开一个“口子”(Socket),双方通过这个口子传输数据。创建Socket时,可以指定网络层使用的是IPv4还是IPv6,传输层用的是TCP还是UDP。
Socket通信过程
这里简单介绍基于TCP协议的Socket程序调用。
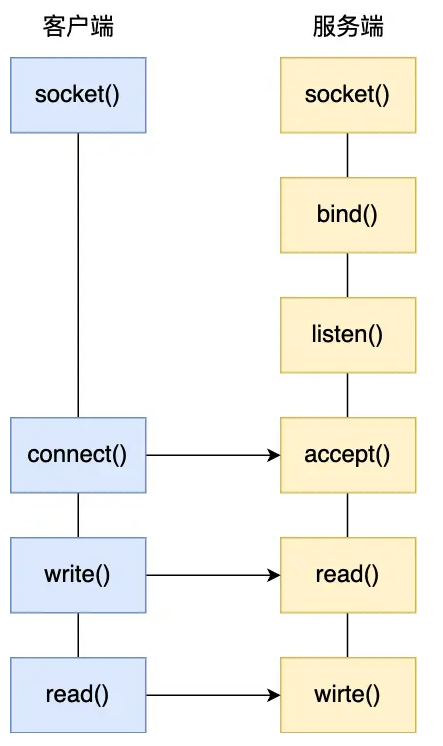
服务端
创建套接字
调用socket()方法,创建指定的网络协议(IPv4)和传输协议(TCP)的Socket。
# Create a socket object
server = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
绑定
调用bind()来绑定IP地址和端口。
# Define the port number
PORT = 5050
# Get the local IP address of the server
SERVER = socket.gethostbyname(socket.gethostname())
ADDR = (SERVER, PORT)
server.bind(ADDR)
监听
服务器套接字调用listen()监听来自客户端的连接请求。
# Start listening for connections
server.listen()
接受连接
服务端进入了监听状态后,通过调用 accept() 函数,来从内核获取客户端的连接,如果没有客户端连接,则会阻塞等待客户端连接的到来。如果建立连接,conn, addr = server.accept() 返回一个新的套接字对象conn(用于与客户端通信)和客户端的地址addr,并且创建一个线程来处理这个连接,这样服务器可以同时处理多个客户端连接。
while True:
# Waiting and accepting for a new connection
# Blocking line of code
conn, addr = server.accept()
# Create a thread for a new client
thread = threading.Thread(target=handle_client, args=(conn, addr))
thread.start()
# Print the number of active connections
print(f"[ACTIVE CONNECTIONS] {threading.active_count() - 1}")
由此可见,监听的 Socket 和真正用来传数据的 Socket 是两个不同的Socket:
- 监听 Socket(Listening Socket):用来等待和接受来自客户端的连接请求。这通常通过调用
bind()方法将套接字绑定到特定的IP地址和端口,然后调用listen()方法来启动监听过程来完成。一旦监听套接字接受了一个连接请求,它就会进行处理,并在内部创建一个新的已连接套接字用于后续的通信。 - 一个叫作已连接 Socket(Connected Socket):连接的双方之间通信的直接渠道。每当服务器监听套接字接受一个新的连接请求时,它就会为每个新的连接创建一个已连接套接字,用于实际的数据传输。每个已连接套接字都有一个唯一的套接字描述符,可以用于标识这个特定的连接。服务器和客户端都将使用这个已连接套接字进行后续的发送和接收操作。
server.accept()部分返回的conn对象实际上就是一个新的已连接套接字。
客户端
客户端在创建好 Socket 后,调用 connect() 函数发起连接,该函数的参数要指明服务端的 IP 地址和端口号,然后开始建立TCP连接。
client = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
client.connect(ADDR)
通信
连接建立后,客户端和服务端就开始相互传输数据了,双方都可以通过 read() 和 write() 函数来读写数据。
-
Server-side
# ... other operations ... # Receiving messages conn.recv(HEADER).decode(FORMAT) # ... other operations ... # Sending ACK conn.send("Msg received".encode(FORMAT)) -
Client-side
message = msg.encode(FORTAM) client.send(message)
完整的实例代码
Server-side:
import socket
import threading
import socket
# Define the header size
# Fist 64 bytes of the message used to receive the message size
HEADER = 64
# Define the port number
PORT = 5050
# Get the local IP address of the server
SERVER = socket.gethostbyname(socket.gethostname())
ADDR = (SERVER, PORT)
# Define the format in which the message will be encoded
FORMAT = 'utf-8'
DISCONNECT_MESSAGE = "!DISCONNECT"
# Create a socket object
server = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
server.bind(ADDR)
def handle_client(conn, addr):
"""
Handle a single client connection
:param conn: socket object
:param addr: tuple of (IP address, port number)
:return: None
"""
print(f"[NEW CONNECTION] {addr} connected.")
connected = True
while connected:
# Receive the message from the client
# Blocking line of code
msg_length = conn.recv(HEADER).decode(FORMAT)
# If the message is not empty
if msg_length:
# Convert the message length to integer
msg_length = int(msg_length)
msg = conn.recv(msg_length).decode(FORMAT)
if msg == DISCONNECT_MESSAGE:
# Close the connection
connected = False
# If the message is not empty
# Print the message
print(f"[{addr}] {msg}")
conn.send("Msg received".encode(FORMAT))
# Close the connection
conn.close()
def start():
"""
Start the server to listen for connections
:return: None
"""
# Start listening for connections
server.listen()
print(f"[LISTENING] Server is listening on {SERVER}")
while True:
# Waiting and accepting for a new connection
# Blocking line of code
conn, addr = server.accept()
# Create a thread for a new client
thread = threading.Thread(target=handle_client, args=(conn, addr))
thread.start()
# Print the number of active connections
print(f"[ACTIVE CONNECTIONS] {threading.active_count() - 1}")
print("[STARTING] Server is starting...")
start()
Client-side
import socket
HEADER = 64
PORT = 5050
FORTAM = 'utf-8'
DISCONNECT_MESSAGE = "!DISCONNECT"
SERVER = socket.gethostbyname(socket.gethostname())
ADDR = (SERVER, PORT)
client = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
client.connect(ADDR)
def send(msg):
"""
Send a message to the server
:param msg: string
:return: None
"""
message = msg.encode(FORTAM)
msg_length = len(message)
send_length = str(msg_length).encode(FORTAM)
send_length += b' ' * (HEADER - len(send_length))
client.send(send_length)
client.send(message)
print(client.recv(2048).decode(FORTAM))
send("Hello World!")
send(DISCONNECT_MESSAGE)
参考资料
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3QiPPX-KeSc
https://xiaolincoding.com/os/8_network_system/selete_poll_epoll.html